A Comparison of Lifting Magnets for Crane

Lifting heavy loads efficiently and safely is a critical requirement in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and warehousing. Cranes, combined with the right type of lifting magnet, offer an effective solution. In this article, we will explore and compare three popular types of lifting magnets: Electromagnetic lifting magnets, permanent lifting magnets, and electro permanent lifting magnets, focusing on their application for crane operations.
Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets
Electromagnetic lifting magnets utilize an electric current passing through a coil to generate a magnetic field. This field attracts and holds ferrous objects, enabling the lifting and moving of heavy loads. These magnets offer numerous advantages, such as their ability to easily control the magnetic field strength, which allows for precise handling of different load sizes and weights. They are ideal for applications that require frequent load changes and varying lifting capacities.
One prominent feature of electromagnetic lifting magnets is that their magnetic force can be completely turned on or off by controlling the electric current. This feature ensures enhanced safety, as the load will remain secure even during a power outage. Electromagnetic lifting magnets are commonly used in scrapyards, warehouses, and recycling facilities where there is a constant need to handle and sort ferrous materials.
Permanent Lifting Magnets
Permanent lifting magnets, on the other hand, rely on permanent magnets to generate a fixed magnetic field. These magnets are renowned for their simplicity, reliability, and absence of any power supply requirements. Permanent lifting magnets are often used for lifting smaller loads that do not require frequent changes in lifting capacity. They are widely employed in metal fabrication, machining, and steel manufacturing industries.
One key advantage of permanent lifting magnets is their cost-effectiveness. Without the need for an electrical power source, they offer long-term savings in energy usage and maintenance. However, their magnetic lifting force cannot be adjusted, making them less suitable for applications that involve frequent load changeovers or varying lifting capacities.
Electro Permanent Lifting Magnets
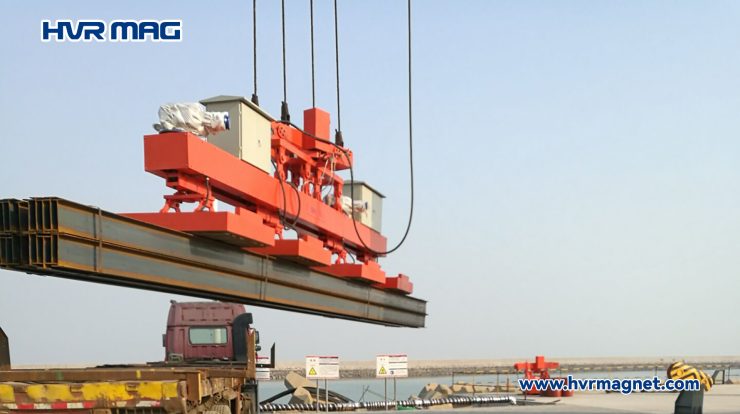
Electro permanent lifting magnets combine the benefits of both electromagnetic and permanent magnets. These magnets use a short electrical pulse to activate the magnet and create a strong magnetic field. Once activated, the magnet retains its magnetic force even if the power supply is disconnected. This feature ensures safety and stability in lifting operations.
The key advantage of electro permanent lifting magnets is their energy-saving capability. Once the magnet achieves full magnetization, it requires no further electrical energy to maintain the lifting force. This feature makes them suitable for remote or outdoor applications where a constant electrical connection may not be available or feasible. Electro permanent lifting magnets are commonly used in steel erection, shipbuilding, and construction activities.
Conclusion
Choosing the right lifting magnet for crane applications depends on various factors such as load capacity, magnet size, lifting height, power requirements, and safety considerations. Electromagnetic lifting magnets offer versatility and precision, making them suitable for applications with variable load sizes. Permanent lifting magnets are cost-effective and reliable for smaller load lifting needs. Electro permanent lifting magnets combine safety, efficiency, and energy-saving features, making them ideal for remote or outdoor applications.
Ultimately, assessing the specific lifting requirements and consulting industry experts or manufacturers will help determine the most appropriate lifting magnet type for a crane setup. Regardless of the chosen type, the proper selection and utilization of lifting magnets ensure efficient and secure operations in lifting and moving heavy loads.
For more information, please contact HVR MAG at export@hvrmagnet.com