A Brief Guide to Powder Metallurgy

What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that involves the production of metal parts or components through the blending, compacting, and sintering of metallic powders.
What is Powder Metallurgy Used for?
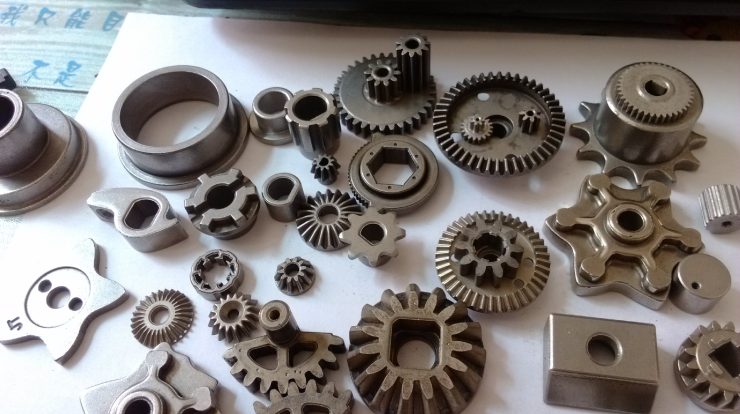
Powder metallurgy finds applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and consumer goods. It is suitable for producing a wide range of components, from simple gears and bearings to complex parts like engine parts or cutting tools.
Procedure of Powder Metallurgy
Powder Production: The first step is to produce the metallic powder. This can be done through various methods such as atomization, electrolysis, or chemical reduction. The goal is to obtain fine and uniform particles of the desired metal or alloy.
Powder Blending: Different powders may be blended together to achieve a desired composition or alloy. This step ensures an even distribution of elements throughout the final product.
Compaction: The blended powder is then poured into a die or mold and subjected to high pressure. This pressure compacts the powder particles, reducing porosity and increasing density. The result is a green compact, which is a solid but still fragile shape.
Sintering: The green compact is transferred to a furnace and subjected to high temperatures. During sintering, the powder particles bond together through diffusion and solid-state reactions. The temperature is carefully controlled to avoid melting the material. Sintering helps to further increase the density of the part and improve its mechanical properties.
Finishing Operations: After sintering, additional post-processing steps may be carried out to improve the surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall performance of the part. These can include machining, heat treatment, plating, or coating.
Inspection and Quality Control: The final products are inspected for dimensional accuracy, mechanical properties, and other quality characteristics to ensure they meet the required specifications.
What are Advantages of Powder Metallurgy?
Design Flexibility: Powder metallurgy allows for the production of complex and intricate shapes that may be challenging or costly to achieve through conventional machining techniques. This flexibility enables the design of parts with tailored geometries and unique features.
Material Efficiency: Powder metallurgy minimizes material waste since the starting materials are in powder form. It allows for the usage of high-cost materials, such as alloys or rare metals, without significant wastage.
Material Control: The process offers precise control over material composition by blending different powders. This enables the production of alloys with specific properties, such as improved strength, corrosion resistance, or thermal conductivity.
Cost-Effectiveness: Powder metallurgy offers cost advantages, especially for mass production. It reduces the need for extensive machining and can yield near-net shape parts, which require minimal additional processing.
Enhanced Material Properties: Sintering helps to achieve a high level of density and solid-state bonding between particles. This results in improved mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Additionally, the process can enhance the material’s resistance to high temperatures or corrosive environments.
Production Efficiency: Powder metallurgy is a highly efficient process, with short production times and high production rates. It can handle large volumes of production and allows for automation, contributing to increased productivity.
Why Magnetic Chuck is Suggested in Powder Metallurgy?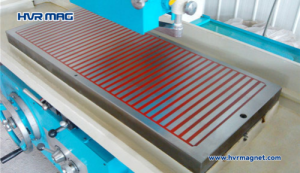
One critical aspect of powder metallurgy is the sintering process, where the compacted metal powder is subjected to elevated temperatures to achieve solidification and bonding. Compared to traditional clamping methods, the ability of electro permanent magnetic chuck to facilitate quick mold changing, enhance worker safety, provide heat-resistant construction, and offer flexibility and versatility highlight their importance in modern manufacturing. As the demand for efficient and safe powder metallurgy sintering continues to rise, the utilization of electro permanent magnetic chucks is poised to play a pivotal role in optimizing production processes and delivering high-quality components.
For more information about magnetic chuck, please contact HVR MAG at export@hvrmagnet.com